|
 Videoconference Room Videoconference Room |
|
|
| Chapter 1 |
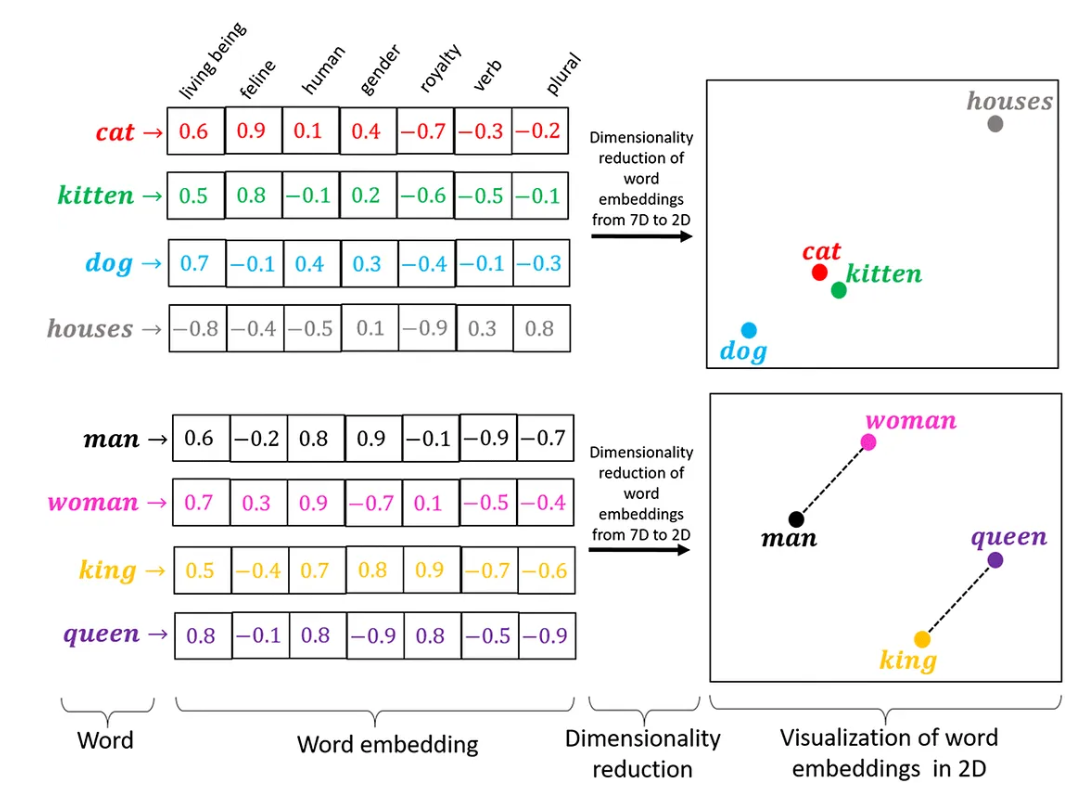
 1.1. What is Computational Linguistics? 1.1. What is Computational Linguistics? |
|
|
 1.2. History of Computational Linguistics 1.2. History of Computational Linguistics |
|
|
 1.3. Core Techniques 1.3. Core Techniques |
|
|
 1.4. Areas of Computational Linguistics 1.4. Areas of Computational Linguistics |
|
|
 1.5. Interdisciplinary Connections 1.5. Interdisciplinary Connections |
|
|
 Explore NLTK packages Explore NLTK packages |
import nltk
nltk.download() |
|
 Let's talk about computational linguistics! My experience in building Siri voices Let's talk about computational linguistics! My experience in building Siri voices |
|
|
 The language of computational linguistics. | Walter Daelemans | TEDxAntwerp The language of computational linguistics. | Walter Daelemans | TEDxAntwerp |
|
|
 Neural network in 5 mins Neural network in 5 mins |
|
|
| Chapter 2 |
 2.1. Word Meaning in Linguistics 2.1. Word Meaning in Linguistics |
|
|
 2.2. Types of Ambiguity 2.2. Types of Ambiguity |
|
|
 2.3. Context and Word Meaning 2.3. Context and Word Meaning |
|
|
 2.4. Wordnet Introduction 2.4. Wordnet Introduction |
|
|
 2.5. Word Sense Disambiguation 2.5. Word Sense Disambiguation |
|
|
 Wordnet Project Homepage Wordnet Project Homepage |
|
|
 Chapter 2 Lecture notes Chapter 2 Lecture notes |
|
|
 Word Sense Disambiguation video lecture Word Sense Disambiguation video lecture |
|
|
 Explore Word Embedding Universe Explore Word Embedding Universe |
|
|
| Chapter 3 |
 3.1. Open versus Closed POS 3.1. Open versus Closed POS |
|
|
 3.2. Markov Models 3.2. Markov Models |
|
|
 3.3. POS Tagging with Python Libraries 3.3. POS Tagging with Python Libraries |
|
|
 Penn Treebank Sample Penn Treebank Sample |
|
|
 Chapter 3 Lecture notes Chapter 3 Lecture notes |
|
|
 Markov Chains Markov Chains |
|
|
 Markov Chains: Generating Sherlock Holmes Stories Markov Chains: Generating Sherlock Holmes Stories |
|
|
 Hidden Markov Model Hidden Markov Model |
|
|
 Forward Algorithm Forward Algorithm |
|
|
 Viterbi Algorithm Viterbi Algorithm |
|
|
 Find difference with Code Beautify Find difference with Code Beautify |
|
|
| Chapter 4 |
 4.1. Decomposing Texts with Bag of Words Model 4.1. Decomposing Texts with Bag of Words Model |
|
|
 4.2. Bayesian Text Classification: The Naive Approach 4.2. Bayesian Text Classification: The Naive Approach |
|
|
 4.3. Support Vector Machines (SVM) 4.3. Support Vector Machines (SVM) |
|
|
 4.4. Decision Trees 4.4. Decision Trees |
|
|
 4.5. Neural Networks 4.5. Neural Networks |
|
|
 Text Classification lecture notes Text Classification lecture notes |
|
|
 Naive Bayes, Clearly Explained!!! Naive Bayes, Clearly Explained!!! |
|
|
 The Kernel Trick in Support Vector Machine (SVM) The Kernel Trick in Support Vector Machine (SVM) |
|
|
 Decision and Classification Trees, Clearly Explained!!! Decision and Classification Trees, Clearly Explained!!! |
|
|
 Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Clearly Explained!!! Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Clearly Explained!!! |
|
|
| Chapter 5 |
 5.1. Constituency Relations 5.1. Constituency Relations |
|
|
 5.2. Dependency Relations 5.2. Dependency Relations |
|
|
 5.3. Treebanks 5.3. Treebanks |
|
|
 Universal Dependencies Project Universal Dependencies Project |
Step 1: Find Query UD treebanks online: Step 2: Try https://lindat.mff.cuni.cz/services/pmltq/#!/treebank/bnc/query/IYWgdg9gJgpgBAbTsAZgVzHAvHA5AOQCVc4BdIA/result/svg?filter=true&timeout=30&limit=100 To explore Vietnamese Universal Dependency Relations, start from here: https://lindat.mff.cuni.cz/services/pmltq/#!/treebank/udvi_vtb214/help
Overview of Parsing Frameworks- Analytical Tree (
a-tree) - Tectogrammatical Tree (
t-tree)
1. Analytical Tree (a-tree):- Definition: Analytical trees represent the surface syntactic structure of a sentence. They show how words are grouped into phrases and how these phrases are related to each other.
- Components:
- Pred (Predicate): The main verb of the sentence.
- Sb (Subject): The subject of the sentence.
- Obj (Object): The object of the sentence.
- AuxP (Auxiliary Preposition): Prepositions that introduce prepositional phrases.
- Atr (Attribute): Modifiers or attributes of nouns.
- Adv (Adverbial): Modifiers or complements of verbs.
- AuxC (Auxiliary Conjunction): Conjunctions that link clauses.
- AuxX: Punctuation markers like commas and periods.
The a-tree in the screenshot breaks down the sentence into its syntactic components, showing hierarchical relationships between words and phrases. 2. Tectogrammatical Tree (t-tree):- Definition: Tectogrammatical trees represent the underlying, deep syntactic structure of a sentence. They abstract away from the surface form to show more semantic and functional relationships.
- Components:
- PRED (Predicate): The main verb of the sentence.
- ACT (Actor): The logical subject or agent of the action.
- PAT (Patient): The logical object or recipient of the action.
- RSTR (Restrictive Attribute): Attributes that provide necessary information about a noun.
- MEANS: Instrumental adjuncts indicating the means by which an action is performed.
- ENUNC (Enunciation): Linking functions that relate to how the sentence is embedded in discourse.
- MANN (Manner): Adverbials expressing the manner of the action.
- APP (Apposition): Noun phrases that are in apposition to another noun phrase.
The t-tree in the screenshot abstracts away from surface syntactic categories to focus on semantic roles and deeper syntactic relationships. Comparison:Analytical Tree: - Focuses on surface syntax.
- Reflects the actual word order and grammatical relationships.
- Useful for syntactic parsing and understanding sentence structure.
Tectogrammatical Tree: - Focuses on deep syntax and semantics.
- Abstracts from surface form to show underlying relationships.
- Useful for semantic parsing and understanding the roles of different sentence elements.
|
|
 Xây dựng treebank tiếng Việt Xây dựng treebank tiếng Việt |
|
|
 Syntax & Grammar Lecture Notes Syntax & Grammar Lecture Notes |
|
|
 Constituency Parsing Constituency Parsing |
|
|
 Dependency parsing Dependency parsing |
|
|
| Chapter 6 |
 6.1. Sources of Text 6.1. Sources of Text |
|
|
 6.2. Sampling Strategies 6.2. Sampling Strategies |
|
|
 6.3. Data Acquisition Techniques 6.3. Data Acquisition Techniques |
|
|
 6.4. Considerations for Representative and Diverse Corpora 6.4. Considerations for Representative and Diverse Corpora |
|
|
 6.5. Corpus Annotation 6.5. Corpus Annotation |
|
|
 6.6. Applications of Annotated Corpora 6.6. Applications of Annotated Corpora |
|
|
 6.7. Best Practices in Building Linguistics Corpora 6.7. Best Practices in Building Linguistics Corpora |
|
|
 Corpus Linguistics Lecture Notes Corpus Linguistics Lecture Notes |
|
|
| Chapter 7 |
 7.1. Introduction 7.1. Introduction |
|
|
 7.2. Core Objectives 7.2. Core Objectives |
|
|
 7.3. Lexical Databases 7.3. Lexical Databases |
|
|
 7.4. Expanding Lexical Resources 7.4. Expanding Lexical Resources |
|
|
 7.5. Automatic Extraction of Lexical Information 7.5. Automatic Extraction of Lexical Information |
|
|
 7.6. Challenges in Computational Lexicography 7.6. Challenges in Computational Lexicography |
|
|
 7.7. Applications of Computational Lexicography 7.7. Applications of Computational Lexicography |
|
|
 Computational Lexicography Lecture Notes Computational Lexicography Lecture Notes |
|
|
| Chapter 8 |
 Introduction Introduction |
|
|
 8.1. Language Teaching 8.1. Language Teaching |
|
|
 8.2. Search Engines and Information Retrieval 8.2. Search Engines and Information Retrieval |
|
|
 8.3. Machine Translation 8.3. Machine Translation |
|
|
 8.4. Sentiment Analysis 8.4. Sentiment Analysis |
|
|
 8.5. Speech Recognition Systems 8.5. Speech Recognition Systems |
|
|
| Chapter 9 |
 Introduction Introduction |
|
|
 9.1. Applications in Healthcare 9.1. Applications in Healthcare |
|
|
 9.2. Applications in Education 9.2. Applications in Education |
|
|
 9.3. Applications in Entertainment and Media 9.3. Applications in Entertainment and Media |
|
|
 9.4. Ethical and Responsible Language Technology 9.4. Ethical and Responsible Language Technology |
|
|
| Resource Center |
 Meet Alpha, your class tutor Meet Alpha, your class tutor |
|
|
 Tools for Research Tools for Research |
|
|
 Past Recordings Past Recordings |
Danh gia LATS Nguyen The Luong https://cloud05.ulearning.vn/playback/presentation/2.3/d4501acd3cda5ff4c87b07008a8de6f7c7cfc6c0-1637738196339
Webinar cua Nguyen Thi Hong Lien cho HVCT: https://cloud05.ulearning.vn/playback/presentation/2.3/eb677b81657eec7b58f1a7ba07e3b5f53bb02689-1642591431195
Vu tap huan cho LAC 7/4/2024: https://cloud05.ulearning.vn/playback/presentation/2.3/aaf9d545548cd1a20da0be92751cdbb8a51af2cd-1720053245124
Lien tap huan cho HVCT 17/1/2022: https://cloud05.ulearning.vn/playback/presentation/2.3/eb677b81657eec7b58f1a7ba07e3b5f53bb02689-1642418216035
Vu tap huan cho HVCT 21/1/2022: https://cloud05.ulearning.vn/playback/presentation/2.3/eb677b81657eec7b58f1a7ba07e3b5f53bb02689-1641986136908
Vu tap huan cho HVCT 14/1/2022: https://cloud05.ulearning.vn/playback/presentation/2.3/eb677b81657eec7b58f1a7ba07e3b5f53bb02689-1642159249548
Vu tap huan cho HVCT 21/1/2022: https://cloud05.ulearning.vn/playback/presentation/2.3/eb677b81657eec7b58f1a7ba07e3b5f53bb02689-1642764009388
Vu tap huan ki nang to chuc hoc va thi truc tuyen: https://cloud05.ulearning.vn/playback/presentation/2.3/2164641e1e2f28b0de3fc7f470774025a7ff3271-1678417085438
eb677b81657eec7b58f1a7ba07e3b5f53bb02689-1642159249548
|
|
 End of course feedback End of course feedback |
|
|
 History of Neural Networks History of Neural Networks |
|
|
 300 possible dimensions in Word Embeddings 300 possible dimensions in Word Embeddings |
|
|
 TARI AI Tools Survey TARI AI Tools Survey |
Please use TARI AI tools at https://tari.huflit.edu.vn before taking this survey. |
|
 Course WhiteBoard Course WhiteBoard |
|
|
 All databases used in the book All databases used in the book |
|